Android dialog is a small window which appears on the screen. It generally provides user with a decisive errata. When you want the users of your application to make any kind of decision or choice then dialog is the best option. It is not meant to occupy the full screen of device. So let us move a little deeper.
4.9.1 Introduction to Android Dialog
Dialogs are generally useful for answering questions, confirming selections, display warnings etc. There are three ways to implement dialogs and they are:
- Dialog Class: Android includes a number of classes which extends Dialog class. Among them the most popular is AlertDialog class. Screens which are based on Dialog class are completely in control of calling activity. There is no need for registration in manifest for this purpose.
- Toasts: BroadcastReceivers and Services generally make use of toast message boxes for displaying the events occurring in background.
- Dialog-themed activities: Dialog theme can be applied to a common activity which would give it a look of standard dialog.
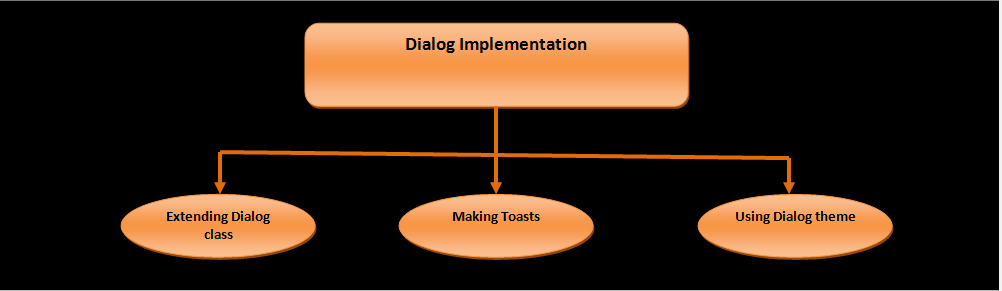
Figure - Three ways of implementing Android dialogs
Android system consists of specialized dialog boxes and they are as follows:
- DatePickerDialog: Users can select date from DatePicker view.
- TimePickerDialog: This dialog allows users to select time from TimePcker View.
- CharacterPickerDialog: Users can select the highlighted character.
- ProgressDialog: This dialog displays progress in dialog box. This is useful for displaying progress of activities. Users can be kept informed about the ongoing process.
So let us create some examples and find out the working of Android dialogs.
Example: Android Dialog box and display progress in dialog
Open your IDE and create a project. Name it as you like. I am naming it as DialogExample app. In this project we shall display one dialog in the parent activity. We shall display progress in dialog in the next activity. Open your activity_main.xml file and code it as shown in the following listing:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context=".MainActivity" > <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Hello Readers!! Press Button to display the dialog" /> <Button android:id="@+id/buttonShowDialog" style="?android:attr/buttonStyleSmall" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:layout_centerVertical="true" android:text="Show Dialog" /> <Button android:id="@+id/buttonNext" style="?android:attr/buttonStyleSmall" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/buttonShowDialog" android:layout_below="@+id/buttonShowDialog" android:layout_marginTop="28dp" android:text="Next" /> </RelativeLayout>
Figure - activity_main.xml file of Android Dialog example
Graphical layout should be similar to the following snapshot:
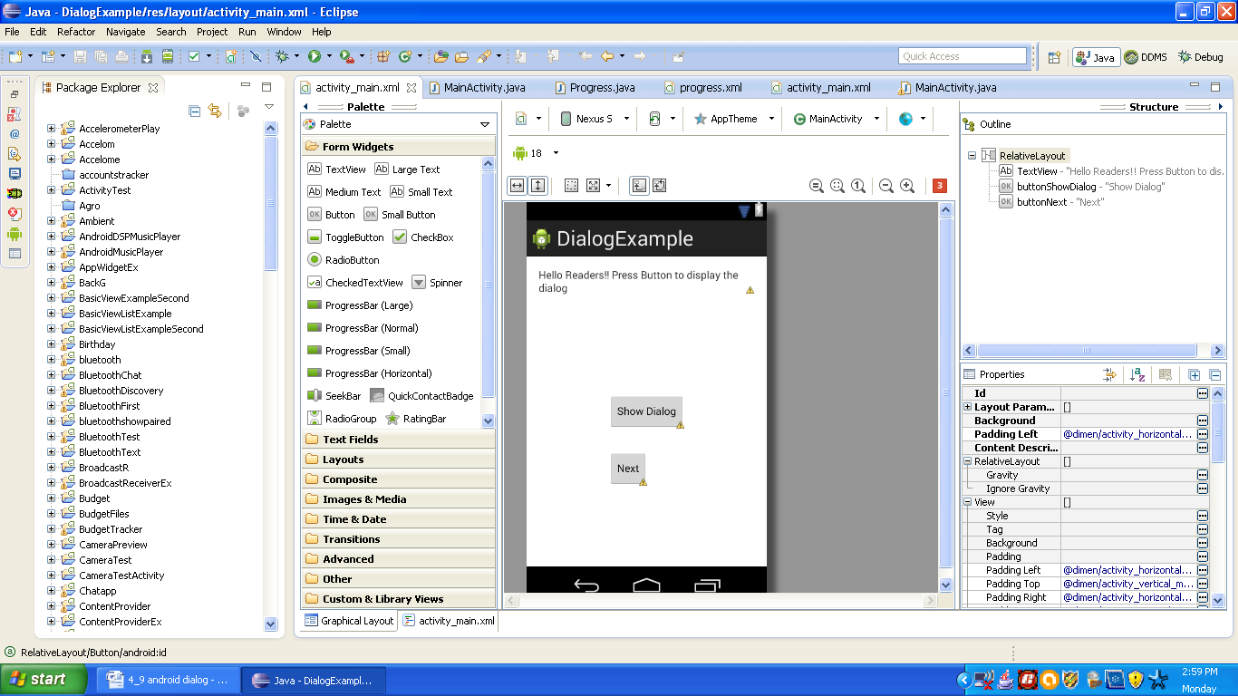
Figure - Graphical layout of Android Dialog Application
Create another xml file and name it progress.xml. Open it and code it as shown in the following listing:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" > <Button android:id="@+id/buttonProgress" style="?android:attr/buttonStyleSmall" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="center" android:text="Progress" /> </LinearLayout>
Figure - progress.xml file
Graphical layout should be similar to the following snapshot:
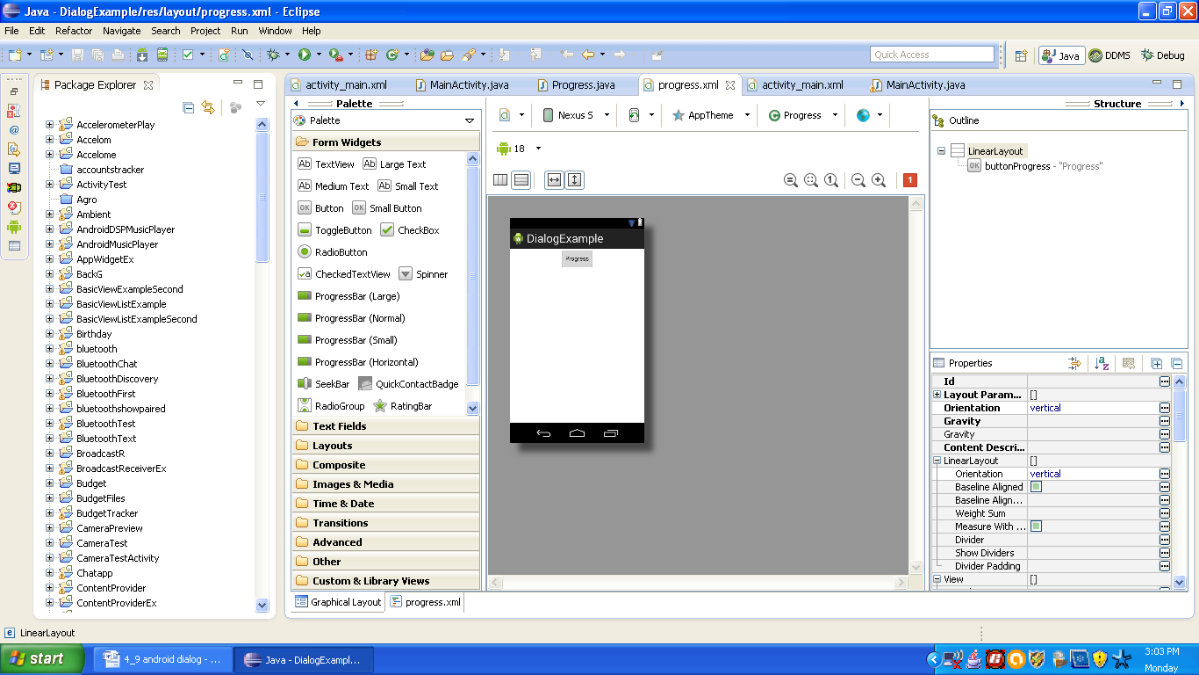
Figure - Graphical layout of progress.xml file
Now open the main activity file and code it as shown in the following listing:
package com.android.tution.Dialog;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.AlertDialog;
import android.app.Dialog;
import android.content.DialogInterface;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
CharSequence[] fruits = { "Apple", "Banana", "Orange", "Grapes" };
boolean[] fruitsChecked = new boolean[fruits.length];
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button next = (Button) findViewById(R.id.buttonNext);
next.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Intent i=new Intent(MainActivity.this,Progress.class);
startActivity(i);
}
});
Button button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.buttonShowDialog);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
showDialog(0);
}
});
}
Figure - First half of code for Android Dialog Application
Continue coding in the same activity and second half of code is as shown in the following listing:
@Override
protected Dialog onCreateDialog(int id) {
switch (id) {
case 0:
return new AlertDialog.Builder(this)
.setIcon(R.drawable.ic_launcher)
.setTitle("Fruit Selection")
.setPositiveButton("Select",
new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog,
int which) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Toast.makeText(getBaseContext(),
"Select button is clicked",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
})
.setNegativeButton("Discard",
new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog,
int which) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Toast.makeText(getBaseContext(),
"Discard button is clicked",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
})
.setMultiChoiceItems(fruits, fruitsChecked,
new DialogInterface.OnMultiChoiceClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog,
int which, boolean isChecked) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Toast.makeText(
getBaseContext(),
fruits[which]
+ (isChecked ? "checked!"
: "unchecked!"),
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}).create();
}
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu);
return true;
}
Figure - Second half of code for Android Dialog Application
We have to connect our progress.xml to a java class and for that create a java class. Name it Progress.java and code it as shown in the following listing:
package com.android.tution.Dialog;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.AlertDialog;
import android.app.Dialog;
import android.app.ProgressDialog;
import android.content.DialogInterface;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class Progress extends Activity {
CharSequence[] cartoons = { "Donald", "Bheem", "Cindrella" };
boolean[] cartoonsChecked = new boolean[cartoons.length];
private ProgressDialog progressDialog;
private int prog = 0;
private Handler progressHandler;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.progress);
Button progress = (Button) findViewById(R.id.buttonProgress);
progress.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
showDialog(1);
prog = 0;
progressDialog.setProgress(0);
progressHandler.sendEmptyMessage(0);
}
});
progressHandler = new Handler() {
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
super.handleMessage(msg);
if (prog >= 100) {
progressDialog.dismiss();
} else {
prog++;
progressDialog.incrementProgressBy(1);
progressHandler.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(0, 100);
}
}
};
}
Figure - First half of Progress.java file
Second half of code is as shown in the following listing:
@Override
protected Dialog onCreateDialog(int id) {
switch (id) {
case 0:
return new AlertDialog.Builder(this)
.setIcon(R.drawable.ic_launcher)
.setTitle("Cartoon Selection")
.setPositiveButton("OK",
new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog,
int which) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Toast.makeText(getBaseContext(),
"OK is clicked", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT)
.show();
}
})
.setNegativeButton("Cancel",
new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog,
int which) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Toast.makeText(getBaseContext(),
"Cancel is clicked",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
})
.setMultiChoiceItems(cartoons, cartoonsChecked,
new DialogInterface.OnMultiChoiceClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog,
int which, boolean isChecked) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Toast.makeText(
getBaseContext(),
cartoons[which]
+ (isChecked ? "checked!"
: "unchecked!"),
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}).create();
case 1:
progressDialog = new ProgressDialog(this);
progressDialog.setIcon(R.drawable.ic_launcher);
progressDialog.setTitle("Simulating Download...");
progressDialog.setProgressStyle(ProgressDialog.STYLE_HORIZONTAL);
progressDialog.setButton(DialogInterface.BUTTON_POSITIVE, "Hide",
new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Toast.makeText(getBaseContext(),
"Hide button is clicked",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
Figure - Second part of progress.java class
Third part of code is as shown in the following listing:
progressDialog.setButton(DialogInterface.BUTTON_NEGATIVE, "Cancel",
new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Toast.makeText(getBaseContext(),
"Clicked Cancel!!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT)
.show();
}
});
return progressDialog;
}
return null;
}
}
Figure - Third part of progress class
Last task is our manifest file. Code it as shown in the following listing:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.android.tution.Dialog" android:versionCode="1" android:versionName="1.0" > <uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="8" android:targetSdkVersion="18" /> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:theme="@style/AppTheme" > <activity android:name="com.android.tution.Dialog.MainActivity" android:label="@string/app_name" > <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> <activity android:name=".Progress" > </activity> </application> </manifest>
Figure - manifest file of Android Dialog Application
