We all read Newspapers, Don’t we? At the very first glimpse, what grabs your attention? The Headlines. Isn’t it? They give us the gist of the news & organize the content.
In the same way, we use headings in HTML to structure the content of our web page.
- A heading element describes about the topic of discussion.
- HTML Heading elements are block level elements i.e., we include them in the body tag, <body>.
- They are very important in HTML documents.
Headings in HTML are defined with the following tags,
- <H1> and </H1>
- <H2> and </H2>
- <H3> and </H3>
- <H4> and </H4>
- <H5> and </H5>
- <H6> and </H6>
Syntax for creating HTML Headings:
<hn>Heading</hn>
where n is any number from 1 to 6.
It should be like this,
<h1> Heading1 </h1>
<h2> Heading2 </h2>
<h3> Heading3 </h3>
<h4> Heading4 </h4>
<h5> Heading5 </h5>
<h6> Heading6 </h6>
<H1> should be preferably used for giving the main title for the page as it displays the content in larger fonts. The size of the font will be decreasing from h1 to h6.The headings are displayed in bold.
Before, learning more about Headings we will look at an example:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title> Learning Headings of HTML </title> </head> <body> <h1> This text is displayed using h1 </h1> <h2> This text is displayed using h2 </h2> <h3> This text is displayed using h3 </h3> <h4> This text is displayed using h4 </h4> <h5> This text is displayed using h5 </h5> <h6> This text is displayed using h6 </h6> </body> </html>
The output of the above program would be
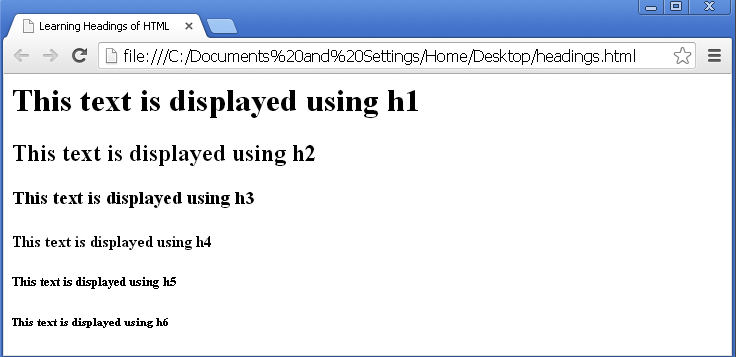
Please notice that, each heading is displayed in a new line even though we did not write code for it.
Attributes for heading elements:
Heading elements support global attributes.
Attributes | Value | Description |
id | Any text | Document wide identifier |
class | Any text | Document wide identifier |
Lang | Any ISO-639 language code | Sets language option for heading |
Dir | rtl, ltr | Sets the direction of text for heading |
Title | Any title | Gives the title for the HTML heading |
Style | Style rules | Defines the presentation of heading |
align | Left, right, center, justify | Defines the alignment of the heading |
ISO-639 language code
This is the value inputted to the lang attribute, which sets the language for the web page or a part of web page. W3C recommends us to declare the language for each web page inside the <html> tag,
International Organization for Standardizations (ISO) classified the languages & gave 2-letter abbreviation in ISO 639-1 standard. According to that the various languages are mentioned using the following codes.
Language | ISO Code |
Abkhazian | Ab |
Afar | Aa |
Afrikaans | Af |
Albanian | Sq |
Amharic | Am |
Arabic | Ar |
Aragonese | An |
Armenian | Hy |
Assamese | As |
Aymara | Ay |
Azerbaijani | Az |
Bashkir | Ba |
Basque | Eu |
Bengali (Bangla) | Bn |
Bhutani | Dz |
Bihari | Bh |
Bislama | Bi |
Breton | Br |
Bulgarian | Bg |
Burmese | My |
Byelorussian (Belarusian) | Be |
Cambodian | Km |
Catalan | Ca |
Chewa | Ny |
Chinese | Zh |
Corsican | Co |
Croatian | Hr |
Czech | Cs |
Danish | Da |
Dutch | Nl |
English | En |
Esperanto | Eo |
Estonian | Et |
Faeroese | Fo |
Farsi | Fa |
Fiji | Fj |
Finnish | Fi |
French | Fr |
Frisian | Fy |
Galician | Gl |
Gaelic (Scottish) | Gd |
Gaelic (Manx) | Gv |
Georgian | Ka |
German | De |
Greek | El |
Greenlandic | Kl |
Guarani | Gn |
Gujarati | Gu |
Haitian Creole | Ht |
Hausa | Ha |
Hebrew | he, iw |
Hindi | Hi |
Hungarian | Hu |
Icelandic | Is |
Ido | Io |
Igbo | Ig |
Indonesian | id, in |
Interlingua | Ia |
Interlingue | Ie |
Inuktitut | Iu |
Inupiak | Ik |
Irish | Ga |
Italian | It |
Japanese | Ja |
Javanese | Jv |
Kannada | Kn |
Kanuri | Kr |
Kashmiri | Ks |
Kazakh | Kk |
Kinyarwanda (Ruanda) | Rw |
Kirghiz | Ky |
Kirundi (Rundi) | Rn |
Korean | Ko |
Kurdish | Ku |
Laothian | Lo |
Latin | La |
Latvian (Lettish) | Lv |
Limburgish ( Limburger) | Li |
Lingala | Ln |
Lithuanian | Lt |
Macedonian | Mk |
Malagasy | Mg |
Malay | Ms |
Malayalam | Ml |
Maltese | Mt |
Maori | Mi |
Marathi | Mr |
Moldavian | Mo |
Mongolian | Mn |
Nauru | Na |
Nepali | Ne |
Norwegian | No |
Occitan | Oc |
Oriya | Or |
Oromo (Afaan Oromo) | Om |
Pashto (Pushto) | Ps |
Polish | Pl |
Portuguese | Pt |
Punjabi | Pa |
Quechua | Qu |
Rhaeto-Romance | Rm |
Romanian | Ro |
Russian | Ru |
Samoan | Sm |
Sangro | Sg |
Sanskrit | Sa |
Serbian | Sr |
Serbo-Croatian | Sh |
Sesotho | St |
Setswana | tn |
Shona | Sn |
Sichuan Yi | Ii |
Sindhi | Sd |
Sinhalese | Si |
Siswati | Ss |
Slovak | Sk |
Slovenian | Sl |
Somali | So |
Spanish | Es |
Sundanese | Su |
Swahili (Kiswahili) | Sw |
Swedish | Sv |
Tagalog | Tl |
Tajik | Tg |
Tamil | Ta |
Tatar | Tt |
Telugu | Te |
Thai | Th |
Tibetan | Bo |
Tigrinya | Ti |
Tonga | To |
Tsonga | Ts |
Turkish | Tr |
Turkmen | Tk |
Twi | Tw |
Uighur | Ug |
Ukrainian | Uk |
Urdu | Ur |
Uzbek | Uz |
Venda | Ve |
Vietnamese | Vi |
Volapk | Vo |
Wallon | Wa |
Welsh | Cy |
Wolof | Wo |
Xhosa | Xh |
Yiddish | yi, ji |
Yoruba | Yo |
Zulu | zu |
The align Attribute:
The align attribute is deprecated in HTML 4.01.Therefore its use is not recommended.
Even though it is not recommended, it will probably work.
The values for align attribute are:
Attribute | Value | Description |
Align (Not supported in HTML5) | Left | Aligns the heading to left |
Right | Aligns the heading to right | |
Center | Aligns the heading to the center | |
Justify | The heading will be justified on both the sides equally |
Example using align attribute:
<html> <head> <title>
Learning Headings with align attribute
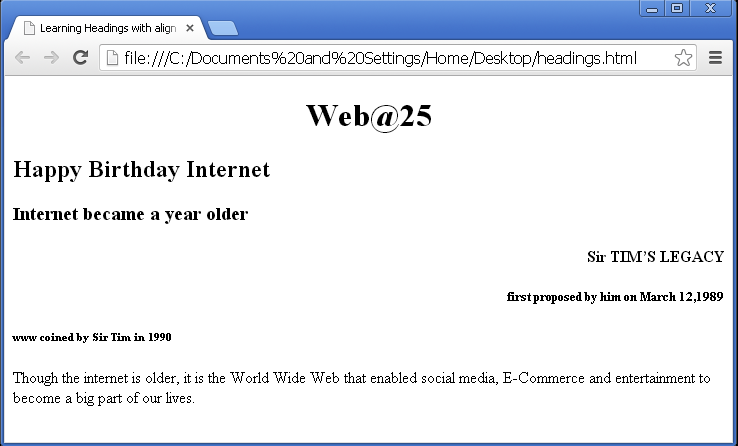
<!DOCTYPE html> <head> <title> </title> </head> <body> <h1 align=center>Web@25</h1> <h2 align=left>Happy Birthday Internet</h2> <h3 align=justify>Internet became a year older</h3> <h4 align=right>Sir TIM’S LEGACY</h4> <h5 align=right>first proposed by him on March 12,1989</h5> <h6>www coined by Sir Tim in 1990</h6> <p> Though the internet is older, it is the World Wide Web that enabled social media, E-Commerce and entertainment to become a big part of our lives.</p> </body> </html>
The output of the above program would be:
Events for Headings:
HTML headings support all event attributes triggered by the browser. For, list of all event attributes you can refer attributes section. Some of the important event attributes supported by HTML headings are:
- onclick
- ondblclick
- onmousedown
- onmouseup
- onmouseover
- onmousemove
- onmouseout
- onkeypress
- onkeydown
- onkeyup
Importance of Headings
Headings are used by search engines to identify words which are important.
Improves SEO
If we use headings appropriately, search engines will give more preference to such pages. Higher the heading the more weight it gets. The heading with H1 has more importance than a heading with H6.
Thus, the headings are used for Search engine optimization (improving the rank & visibility of our web page).
Improves Accessibility
Many screen readers & assistive devices meant for visually impaired people use headings for skimming the web pages. We can go to relevant content by using headings without reading the whole page.
Please do Remember,
- Always use the appropriate ending tag.
- Do not use heading tags for styling the content.
- Use them for what they are intended (for giving headings)
- Do not break the hierarchy of headings i.e., always follow the order h1, h2, h3, h4, h6.
- Skipping the order of headings makes the page look unorganized.
- Always use H1 as main heading tag.
- If possible, use only one H1 for a single page.
- Headings put line breaks for us, so no need to use separate tags.
- The size & look of the font will depend on the browser , the result may be varying according to the type of browser.
In the next chapter, we will learn about Paragraphs in HTML.
