14.1 Overview of JDBC batch processing
In earlier chapters we discussed how to execute the Queries on a database using Statement and Prepared Statements. When we execute any query to database, there are certain operations take place at backend like opening connection/ closing connection which we used to handle but opening and closing of connections are expensive.
Also sometimes we would need to execute several statements in a batch which means we can save the database calls. Both Statement and PreparedStatement supports batch updates.
By default the auto-commit mode of a JDBC Connection is true which means database commits everything to database after every Data manipulations statement.
Whenever we execute batch statements, we must set the auto-commit mode to false.
14.2 JDBC Batch Processing API
As mentioned above, both Statement and PreparedStatements supports batch processing. To do so, there are below methods-
- addBatch(String Sql) – This is an API for Statement and it takes an String which is SQL which need to be fired to database and will be added to batch.
- addBatch() – This is an API for PreparedStatement
- int[ ] executeBatch() – This is an API for both PreparedStatement and Statement and is used to execute the SQL statements added in a batch. As a result, this method returns an array of integers which contains number of rows affected corresponding to each batch statement.
- clearBatch() – This API is used to clear all the batch statements added.
14.3 JDBC Batch Examples
We will use the MySQL database .
- Use the below sql statement to create a schema
Create schema JDBCTutorial;
- Create table User with 4 columns using below SQL
CREATE TABLE `User` ( `id` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT , `name` VARCHAR(45) NULL , `age` VARCHAR(45) NULL , `email` VARCHAR(45) NULL , PRIMARY KEY (`id`) );
14.3.1 – Write and Example to insert the new Users in a batch processing using Statement.
Solution –
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class BatchInsertExample {
public static void main(String args[])
{
try
{
Connection conn= getConnection();
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
String sql = "insert into User (name, age , email) values ('User10', '23','u10@gmail.com')";
stmt.addBatch(sql);
sql = "insert into User (name, age , email) values ('User11', '24','u11@gmail.com')";
stmt.addBatch(sql);
sql = "insert into User (name, age , email) values ('User12', '24','u12@gmail.com')";
stmt.addBatch(sql);
sql = "insert into User (name, age , email) values ('User13', '24','u13@gmail.com')";
stmt.addBatch(sql);
stmt.executeBatch();
conn.commit();
stmt.close();
conn.close();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static Connection getConnection() {
Connection con = null;
String dbDriver = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
String dbUsername = "root";
String dbPassword="password";
String dbHostname="localhost";
String dbPort="3306";
String schema="JdbcTutorial";
try {
String url = "jdbc:mysql://"+dbHostname+":"+dbPort+"/"+schema;
Class.forName(dbDriver);
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, dbUsername, dbPassword);
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex1)
{
System.out.println("Failed to find driver class " + ex1.getMessage());
System.exit(1);
}
catch (SQLException ex2) {
System.out.println("Connection failed " + ex2.getMessage());
System.exit(2);
}
return con;
}
}
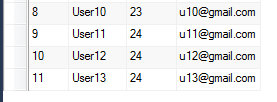
On Running the above program, it will insert four new users. Refer below
14.3.2 – Write and Example to insert the new Users in a batch processing using Prepared Statement.
Solution –
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class BatchInsertExample {
public static void main(String args[])
{
try
{
Connection conn= getConnection();
String sql = "insert into User (name, age , email) values (?,?,?)";
PreparedStatement stmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
stmt.setString(1,"User10");
stmt.setString(2,"23");
stmt.setString(3,"u10@gmail.com");
stmt.addBatch();
stmt.setString(1,"User11");
stmt.setString(2,"24");
stmt.setString(3,"u11@gmail.com");
stmt.addBatch();
stmt.setString(1,"User12");
stmt.setString(2,"24");
stmt.setString(3,"u12@gmail.com");
stmt.addBatch();
stmt.setString(1,"User13");
stmt.setString(2,"24");
stmt.setString(3,"u13@gmail.com");
stmt.addBatch();
stmt.executeBatch();
conn.commit();
stmt.close();
conn.close();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static Connection getConnection() {
Connection con = null;
String dbDriver = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
String dbUsername = "root";
String dbPassword="password";
String dbHostname="localhost";
String dbPort="3306";
String schema="JdbcTutorial";
try {
String url = "jdbc:mysql://"+dbHostname+":"+dbPort+"/"+schema;
Class.forName(dbDriver);
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, dbUsername, dbPassword);
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex1)
{
System.out.println("Failed to find driver class " + ex1.getMessage());
System.exit(1);
}
catch (SQLException ex2) {
System.out.println("Connection failed " + ex2.getMessage());
System.exit(2);
}
return con;
}
}
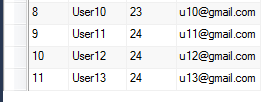
On running the above program, it will insert four new users. Refer below