List Class
This class extends the Screen class and implements the interface Choice. This object allows us to create screens with a list of options to select.
The List class has two constructors:
List(String title, int listType)
List(String title, int listType, String[] elements, Image[] images)
The listType defines which type of List we want to create an can be: EXLUSIVE, MULTIPLE and IMPLICIT.
An exclusive List, means that only one option can be selected.
An implicit List, means that the selection of an option triggers an event.
A multiple List, means that many options can be selected at the same time.
Let’s create a MIDlet with an EXCLUSIVE list.
package my.demo;
import javax.microedition.lcdui.Command;
import javax.microedition.lcdui.CommandListener;
import javax.microedition.lcdui.Display;
import javax.microedition.lcdui.Displayable;
import javax.microedition.lcdui.Form;
import javax.microedition.lcdui.List;
import javax.microedition.midlet.MIDlet;
import javax.microedition.midlet.MIDletStateChangeException;
public class HelloWorld extends MIDlet implements CommandListener {
private Display myDisplay;
private Form formOptionSelected;
private Command exitCommand = new Command("Exit", Command.EXIT,1);
private Command backCommand = new Command("Back", Command.BACK,1);
private Command selectCommand = new Command("Select", Command.OK,1);
private String[] options = {"Option A","Option B", "Option C"};
private List myList;
public HelloWorld() {
myDisplay = Display.getDisplay(this);
myList = new List("Menu", List.EXCLUSIVE, options, null);
myList.addCommand(exitCommand);
myList.addCommand(selectCommand);
myList.setCommandListener(this);
}
protected void destroyApp(boolean arg0) throws MIDletStateChangeException {
notifyDestroyed();
}
protected void pauseApp() {
}
protected void startApp() throws MIDletStateChangeException {
myDisplay.setCurrent(myList);
}
public void commandAction(Command c, Displayable d) {
if (c==exitCommand) {
System.out.println("Exit");
try {
destroyApp(false);
} catch (MIDletStateChangeException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else if (c==backCommand) {
myDisplay.setCurrent(myList);
System.out.println("Back");
} else if (c==selectCommand) {
System.out.println("List");
formOptionSelected = new Form ("Option selected: " + options[myList.getSelectedIndex()]);
formOptionSelected.addCommand(backCommand);
formOptionSelected.setCommandListener(this);
myDisplay.setCurrent(formOptionSelected);
}
}
}
When executing this MIDlet, our initial screen will show something like this:
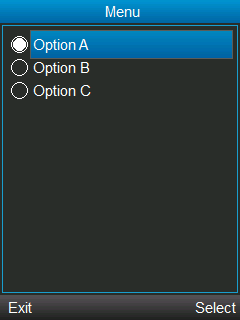
When selecting Option A, and pressing the Select event, the following screen is displayed:

When selecting Option B, and pressing the Select event, the following screen is displayed:

When selecting Option C, and pressing the Select event, the following screen is displayed:

Now, let’s create a MIDlet with an IMPLICIT list.
package my.demo;
import javax.microedition.lcdui.Command;
import javax.microedition.lcdui.CommandListener;
import javax.microedition.lcdui.Display;
import javax.microedition.lcdui.Displayable;
import javax.microedition.lcdui.Form;
import javax.microedition.lcdui.List;
import javax.microedition.midlet.MIDlet;
import javax.microedition.midlet.MIDletStateChangeException;
public class HelloWorld extends MIDlet implements CommandListener {
private Display myDisplay;
private Form formOption1, formOption2;
private Command exitCommand = new Command("Exit", Command.EXIT,1);
private Command backCommand = new Command("Back", Command.BACK,1);
private List myList;
public HelloWorld() {
myDisplay = Display.getDisplay(this);
myList = new List("Menu", List.IMPLICIT);
myList.insert(0, "Option2", null);
myList.insert(0, "Option1", null);
myList.addCommand(exitCommand);
formOption1= new Form("Option 1");
formOption2= new Form("Option 2");
formOption1.addCommand(backCommand);
formOption2.addCommand(backCommand);
myList.setCommandListener(this);
formOption1.setCommandListener(this);
formOption2.setCommandListener(this);
}
protected void destroyApp(boolean arg0) throws MIDletStateChangeException {
notifyDestroyed();
}
protected void pauseApp() {
}
protected void startApp() throws MIDletStateChangeException {
myDisplay.setCurrent(myList);
}
public void commandAction(Command c, Displayable d) {
if (c==exitCommand) {
System.out.println("Exit");
try {
destroyApp(false);
} catch (MIDletStateChangeException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else if (c==backCommand) {
myDisplay.setCurrent(myList);
System.out.println("Back");
} else if (c==myList.SELECT_COMMAND) {
System.out.println("List");
switch (myList.getSelectedIndex()) {
case 0: {
myDisplay.setCurrent(formOption1);
break;
}
case 1: {
myDisplay.setCurrent(formOption2);
break;
}
}
}
}
}
When executing this MIDlet, our initial screen will show something like this:
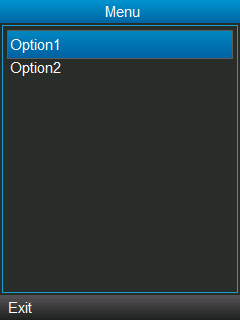
If you go to Option 1 and select it, the following screen will be displayed:

If you select Back, you will be taken to the initial screen.
If you go to Option 2 and select it, the following screen will be displayed:

Finally, let’s create a MIDlet with an MULTIPLE list.
package my.demo;
import javax.microedition.lcdui.Command;
import javax.microedition.lcdui.CommandListener;
import javax.microedition.lcdui.Display;
import javax.microedition.lcdui.Displayable;
import javax.microedition.lcdui.Form;
import javax.microedition.lcdui.List;
import javax.microedition.midlet.MIDlet;
import javax.microedition.midlet.MIDletStateChangeException;
public class HelloWorld extends MIDlet implements CommandListener {
private Display myDisplay;
private Form formOptionSelected;
private Command exitCommand = new Command("Exit", Command.EXIT,1);
private Command backCommand = new Command("Back", Command.BACK,1);
private Command selectCommand = new Command("Select", Command.OK,1);
private String[] options = {"Option A","Option B", "Option C"};
private List myList;
public HelloWorld() {
myDisplay = Display.getDisplay(this);
myList = new List("Menu", List.MULTIPLE, options, null);
myList.addCommand(exitCommand);
myList.addCommand(selectCommand);
myList.setCommandListener(this);
}
protected void destroyApp(boolean arg0) throws MIDletStateChangeException {
notifyDestroyed();
}
protected void pauseApp() {
}
protected void startApp() throws MIDletStateChangeException {
myDisplay.setCurrent(myList);
}
public void commandAction(Command c, Displayable d) {
if (c==exitCommand) {
try {
destroyApp(false);
} catch (MIDletStateChangeException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else if (c==backCommand) {
myDisplay.setCurrent(myList);
} else if (c==selectCommand) {
String selectedOptions = "";
boolean[] selectedItems = new boolean[myList.size()];
myList.getSelectedFlags(selectedItems);
for (int i=0;i<myList.size();i++) {
if (selectedItems[i]) {
selectedOptions = selectedOptions + options[i] + "\n";
}
}
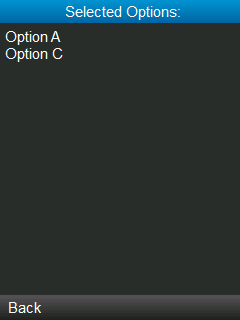
formOptionSelected = new Form ("Selected Options:");
formOptionSelected.append(selectedOptions);
formOptionSelected.addCommand(backCommand);
formOptionSelected.setCommandListener(this);
myDisplay.setCurrent(formOptionSelected);
}
}
}
When executing this MIDlet, our initial screen will show something like this:
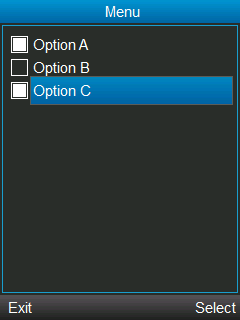
When you select multiple options and hit on the Select command, a new screen will be shown listing all the options selected.